oc create -f https://radanalytics.io/assets/zeppelin-example/zeppelin-openshift.yaml
Deploying Apache Zeppelin notebooks
Introduction
Apache Zeppelin is an alternative to project Jupyter to provide a notebook to run analysis over data and plot graphs in order to show to end users an overview about the data or even doing some exploratory analysis and plot some graphs using the data.
This example shows how to use the Zeppelin OpenShift template created to run on top of OpenShift, as well as provide an example notebook to run on top of your OpenShift cluster.
Architecture
The central piece is the Apache Zeppelin pod, used to create notebooks. From Zeppelin we will connect to the Spark cluster managed by the Oshinko project and run some analysis. This example will use a pod for the Zeppelin instance and two other pods for the Apache Spark cluster (1 master and 1 worker).
Installation
Installing this notebook is straightforward; you simply need to create an OpenShift project, deploy a Spark cluster in that project, and install and run the notebook image.
Prerequisites
Follow the Get Started instructions to create an OpenShift project with the Oshinko web interface running.
Setting up a cluster
From the OpenShift developer console, visit the Oshinko web interface. Use the interface to create a new cluster, and take note of what you’ve called this cluster.
Setting up the Zeppelin template
In the same project, add the Zeppelin template with the following command:
After adding the template, create the Zeppelin application with the following command:
oc new-app --template=$namespace/apache-zeppelin-openshift \
--param=APPLICATION_NAME=apache-zeppelin \
--param=GIT_URI=https://github.com/rimolive/zeppelin-notebooks.git \
--param=ZEPPELIN_INTERPRETERS=md
After running the command above, a build will be triggered to add the notebooks hosted in the Git repository specified in the GIT_URI parameter, as well as copy the configuration files and install the md interpreter. The md interpreter is used to write Markdown blocks in zeppelin.
When the build finishes, it will deploy the newly built Zeppelin image. Click on the hostname defined in the apache-zeppelin app. In case you don’t see a URL for Zeppelin, check if a route is create with the command:
oc get route
Usage
Apache Zeppelin can create powerful notebooks to run exploratory analysis from the data you want to handle, as well as design dashboards to monitor the quality of your data or measurements that will drive a decision based on what is analyzed.
When you access the Zeppelin app, you will see a Untitled Note 1 notebook. This is
the example notebook from the GitHub repo specified in the GIT_URI parameter:

When you open the notebook, you will see some paragraphs (some are Markdown and others
are Python). You can run individually each paragraphs or you can click on the Run all
paragraphs button to run the whole notebook. Just for learning purpose, I’d suggest
run all paragraphs and see the result:
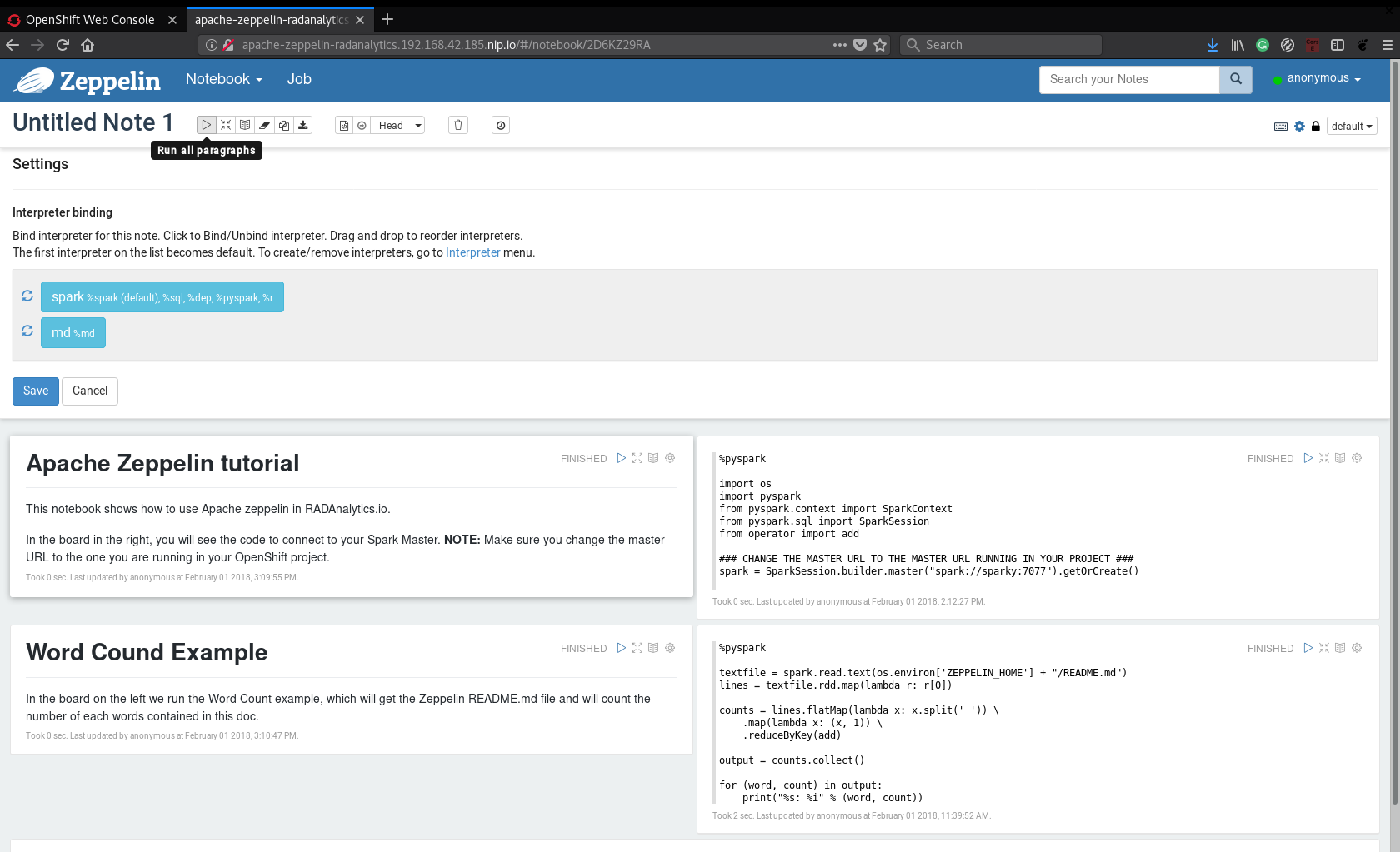
This notebook will connect to the Apache Spark cluster, create an RDD based on data(in the example notebook, the Apache Zeppelin README.md file) and run a simple word count. All processing will be run on the Spark cluster.
Expansion
To make the example better, the notebook can add some plots to show the data, as well as use forms to make the plots interactive.
Videos
There is no video for this application at this time