oc new-app --template radanalytics-jupyter-notebook \ -p NAME=my-notebook \ -p JUPYTER_NOTEBOOK_PASSWORD=secret
How do I launch a Jupyter notebook on OpenShift?
There are multiple ways to launch a Jupyter notebook on OpenShift with the
radanalytics.io tooling. You can use the OpenShift console or the oc command
line tool. Before running these instructions, you will need to have installed
the radanalytics.io manifest as referenced on the
Get Started page.
Launching Jupyter from the OpenShift console
To begin, select the "Jupyter Notebook" template from the "Add to Project" menu in your OpenShift console.
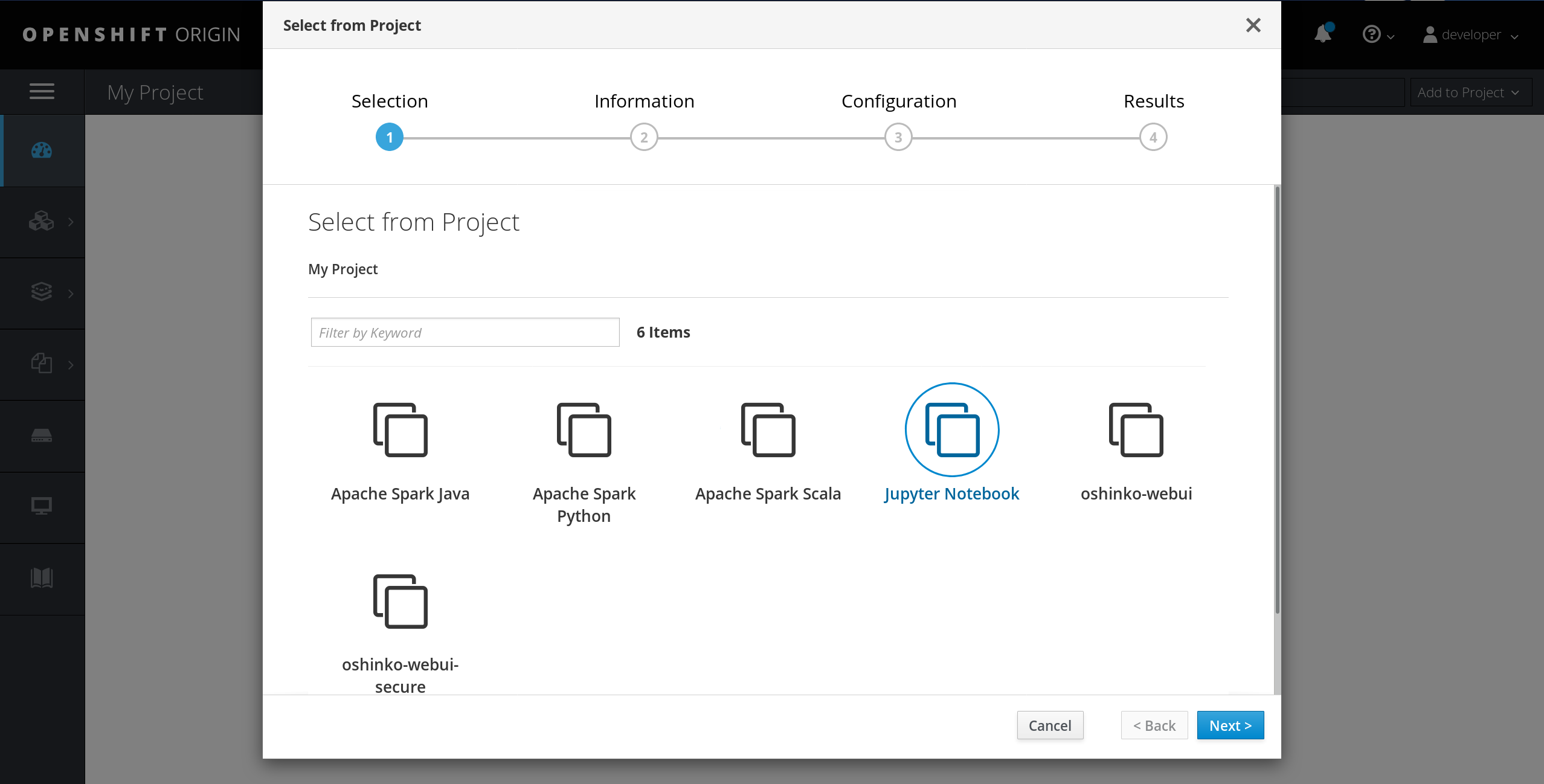
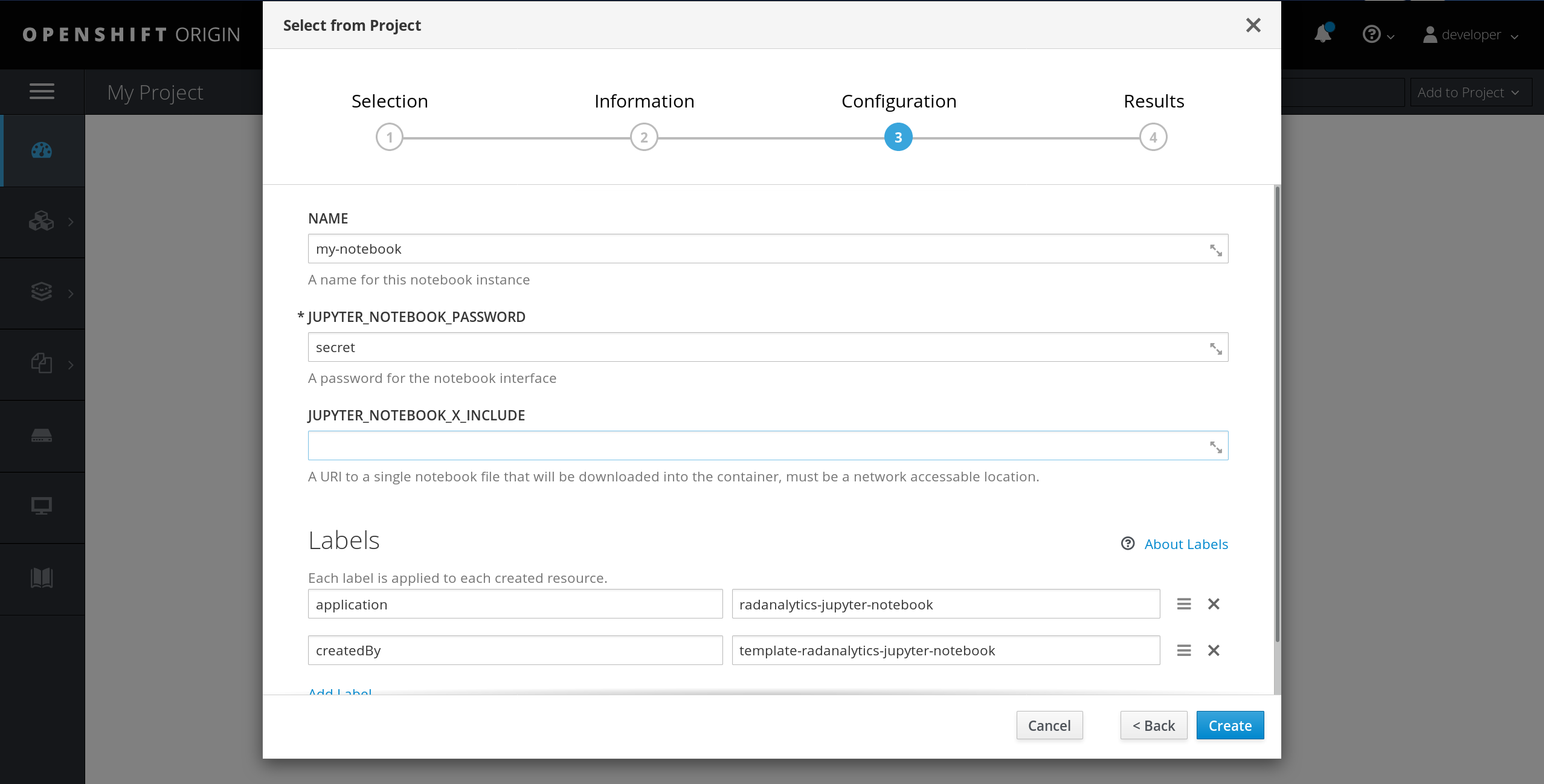
After selecting the template and clicking past the information screen, you will be presented with several options for your notebook deployment. You will need to create a password for your notebook and optionally give it a name and the URI of an IPython notebook file to download.
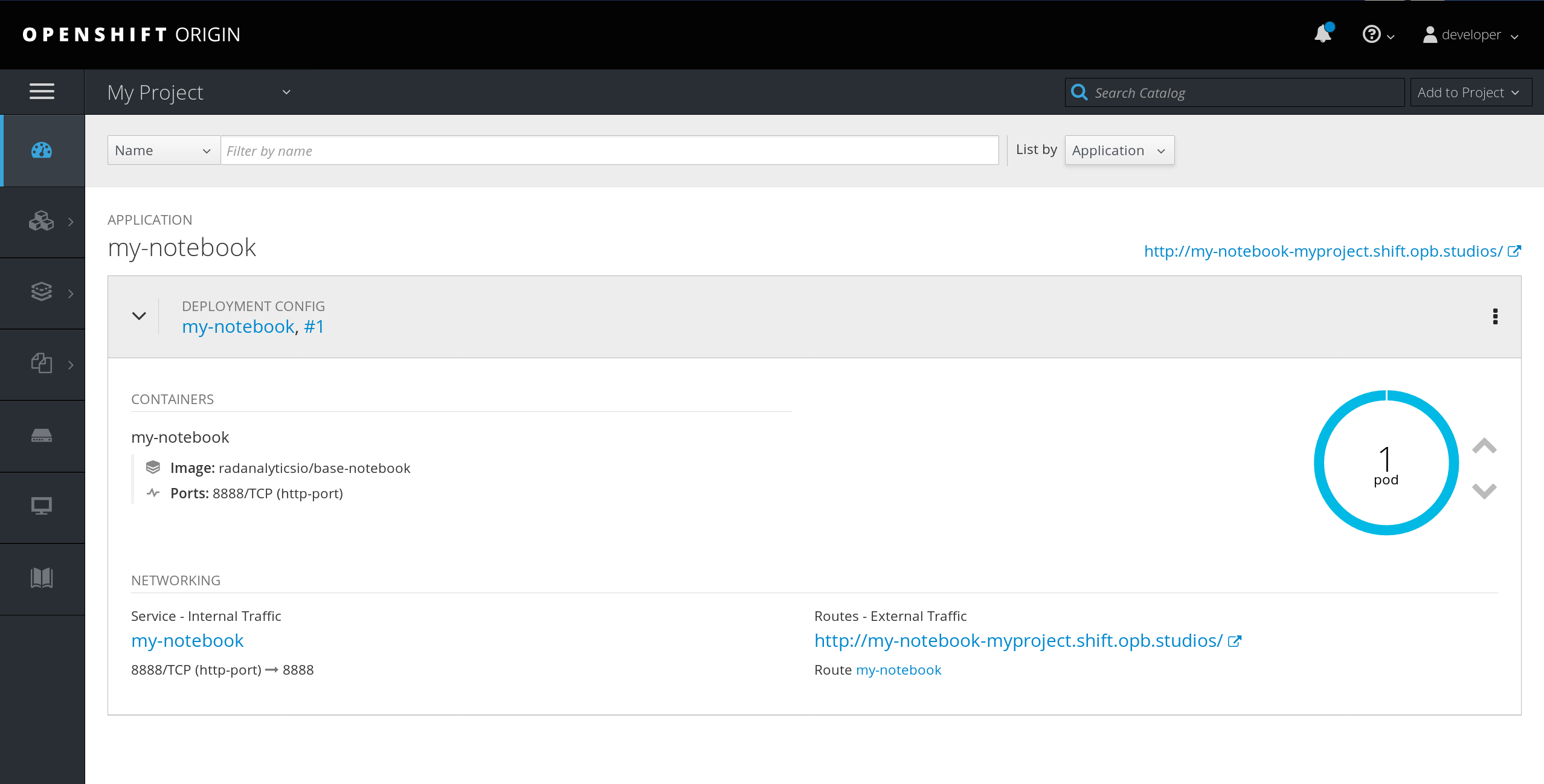
After clicking "create" you will see the application deploy in your OpenShift project, simply click on the route link created and you will be directed to the notebook.
Launching Jupyter from the command line
There are two methods for launching a Jupyter notebook from the command line:
by using the template or directly with oc new-app and the container image.
Template launch
The following command line will launch the template and create the necessary route to access your notebook. Please note that you can change the parameter options to customize your notebook launch.
To pass a notebook URI, simply add the
-p JUPYTER_NOTEBOOK_X_INCLUDE=<your URI> argument to your command.
Image launch
If you prefer a lower level option for creating your notebook, or have other details that you need to specify, you can create the notebook directly from the image source. To do this, simply use the following command:
oc new-app radanalyticsio/base-notebook \ --name my-notebook \ -e JUPYTER_NOTEBOOK_PASSWORD=secret
Please note, in this example you will need to use the environment variable
option (-e or --env) for the JUPYTER_NOTEBOOK_PASSWORD and
JUPYTER_NOTEBOOK_X_INCLUDE arguments.
You will also need to manually create the route for the notebook.